|
侾丏Activation and inactivation processes of cell viability by atmospheric pressure plasma flow
We have now studied about the activation and inactivation mechanism of
cell viability by a plasma flow, and the transport mechanism of chemical
species generated by the plasma flow. T. Sato et al., J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 44 (2011), 372001 M. Yokoyama et al., BBRC, 450 (2014), 1266 T.
Miyahara et al., AIP Advances, 4 (2014), 047115 |
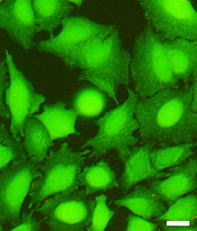 丂 丂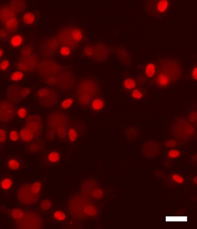 Fluorescence image of HeLa cells. Regular (Left). Cell death after exposure (Right). 丂 |
俀丏Sterilization device and mechanism by low-temperature plasma at atmospheric pressure
仜 Microwave argon plasma flow
To reduce infection risks of new influenza, nosocomial infection and so
on, and to develop next-generation medical instruments, we aim at clarifying
generation and transportation mechanisms of a plasma flow by experimental
and computational analyses and we also aim at identifying the central factor
of sterilization effect and clarifying sterilization mechanism.
For Further Details:
T. Sato et al., Applied Physics Letters, 89 (2006), 073902.
T. Sato et al., IEEE Trans. Industry Appli., 42 (2006), 399.
T. Sato et al., IEEE Trans. Industry Appli., 43 (2007), 1159.
T. Miyahara et. al, Europhysics Letters, 86 (2009), 45001.
T. Sato et al., New Journal of Physics, 11 (2009), 115018.
(International Patent Application)
PCT/JP2005/15431,
Special Application 2007-001999,
Patent 2008-06604
 丂
丂
Photograph丂丂 丂丂N2*
丂丂丂丂丂Visualization
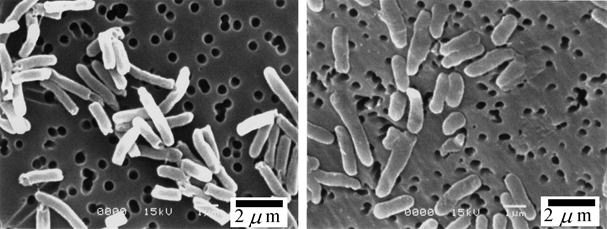
Effect of plasma flow on E coli. Treated (R)
仜 Sterilization in a tube
Application to medical equipments such as catheter sterilization by radical
generation, transport and concentration using plasma flow control. For
example, optimum sterilization conditions are 5 min, 70 亷 and 13 W for
a tube of 100 mm length and 3 mm i.d.
For Further Details:
T. Sato et al., Plasma Processes and Polymers, 5 (2008), 606.
T. Sato et al.., IEEE Trans. Industry Appli., 45 (2009) , 44.
Patent No.4898635, No.4902842
(International Patent Application)
PCT/JP2006/315958,
Special Application 2005-270014,
Special Application 2006-220400,
etc.
 丂丂丂
丂丂丂
Twin voltex丂丂丂丂丂N2* emission
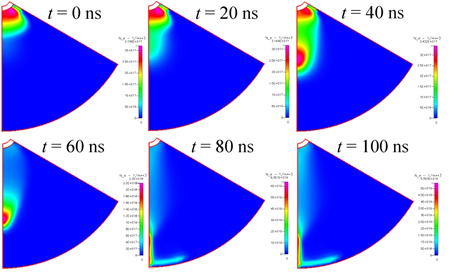
Computational analysis of streamer propagation
仜 Plasma autoclave
Development of steam sterilization system for medical equipments at 100亷
and atmospheric pressure by controlling OH radical generation and transport.
We succeeded in sterilizing bacteria spores within 30 min.
For Further Details:
T. Furui, T. Sato, JSME Journal B, 70 (2008), 879. (in Japanese)
Patent No.4881249
Page top
 丂
丂
Steam plasma flow
俁丏Initiation and propagation mechanism of underwater streamers
仜 We aim at developing underwater plasma generation device for cell irradiation
by clarifying and controlling underwater microscopic high-speed discharge
phenomena.
We clarified that a primary streamer propagated intermittently synchronized
with appearance of pulsed currents and a secondary streamer propagated
with around 20 km/s during a continuous current appears.
For Further Details:
H. Fujita et al., J. Appl. Phys. 113 (2013), 113304.
H. Fujita et al., EPL, 105 (2014), 15003.
H. Fujita et al., IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 42 (2014), 2398.
H. Fujita et al., J. Appl. Phys. 116 (2014), 213301.
H. Fujita et al., Journal of the Institute of Electrostatics Japan, 39 (2015), 21. (Institute of Electrostatics Japan Paper Award)
Page top
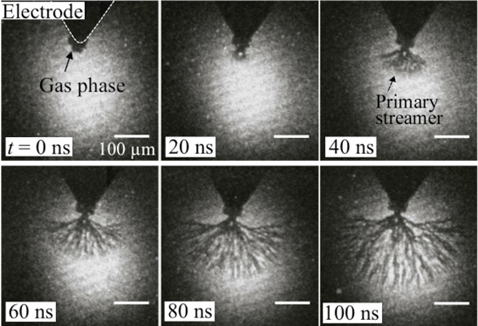
Propagation of underwater primary streamer
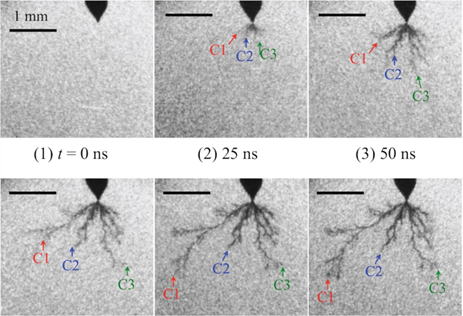
Propagation of underwater secondary streamer
係丏Behavior of plasma-induced cavitation bubbles
仜 We conduct a fundamental research toward the development of underwater plasma medical devices by clarifying the rebound behavior of the bubbles generated by underwater plasma.
We have clarified that the rebound behavior changes because the hydrogen
gas is generated at the time of bubble generation by using high heat source
such as laser or spark, and that the hydrogen gas is introduced into the
bubbles, through the collaborative research with Professor Farhat's group
at Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne (EPFL, Switzerland).
For Further Details:
T.
Sato et al., APL102 (2013), 074105.
Page top
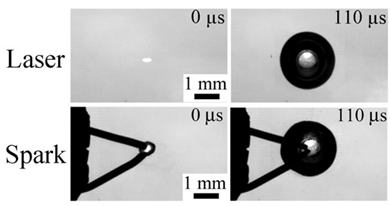
Behavior of bubbles generated in water
俆丏Chemical transport by plasma actuator
仜 We clarify chemical transport mediating gas-liquid interface and aim for an application to plasma medicine.
We have clarified that the plasma generated on the water surface forms
thermal flow field in the gas phase and the flow is induced under water,
and that the chemical species generated in the gas phase dissolve in water
and are transported mainly by convection flow, through the collaborative
research with Professor Morfill's group at Max-Planck Institute (Germany).
We have also clarified the details of the generation mechanism of induced
flows by plasma
For Further Details:
T. Shimizu et al., New J. Phys., 13 (2011), 053025.
T.
Shimizu et al., J. Photochem.
Sci. Tech., 24 (2011), 421R.
Page top
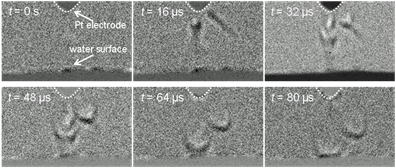
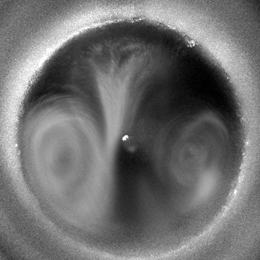
High speed images of plasma induced flow in the plasma-water system.