HOME > Researches List > Super-lean burn
Researches
Super-lean burn
Recently, the improvement of a thermal efficiency with spark-ignited engines, which widely used for automobiles, is required for efficient use of fossil fuels. In order to improve the thermal efficiency, lean burn which uses the mixture with lower fuel/air ratio than ordinary one is focused on. The lean burn enables to improve the theoretical thermal efficiency with an increase in specific heat ratio of the mixture and the indicated thermal efficiency with a decrease in heat loss because the combustion temperature drops in the engine. Recent studies have reported that a potential relationship between lean operation limit of practical engine and laminar burning velocity of the mixture. Therefore, “the super-lean burn” using the fuel with high burning velocity is expected, which operates with lower fuel/air ratio than ordinary lean burn combustion. In order to realize the engine operation under super-lean condition using extremely fuel-lean mixture, it is essential to introduce highly turbulence into the engine. However, the difficulty to ignite the fuel-lean mixture at the intense turbulent condition has been reported.
For understanding of the fundamental combustion characteristics of fuel with the high burning rate and the ignition difficulty under the highly turbulence, the observation of ignition phenomena under highly turbulent conditions and the measurements of laminar burning velocity have been conducted using a combustion vessel with counter-rotating fans. These observations are expected to clarify the innovative method to ignite the fuel-lean mixture in the intense turbulent condition and the relationship between lean operation limit and laminar burning velocity, contributing the engine operation using super-lean burn.
Projects participated:SIP "Innovative combustion technology"
Ignition of fuel-lean mixture (left: laminar, right: turbulent)
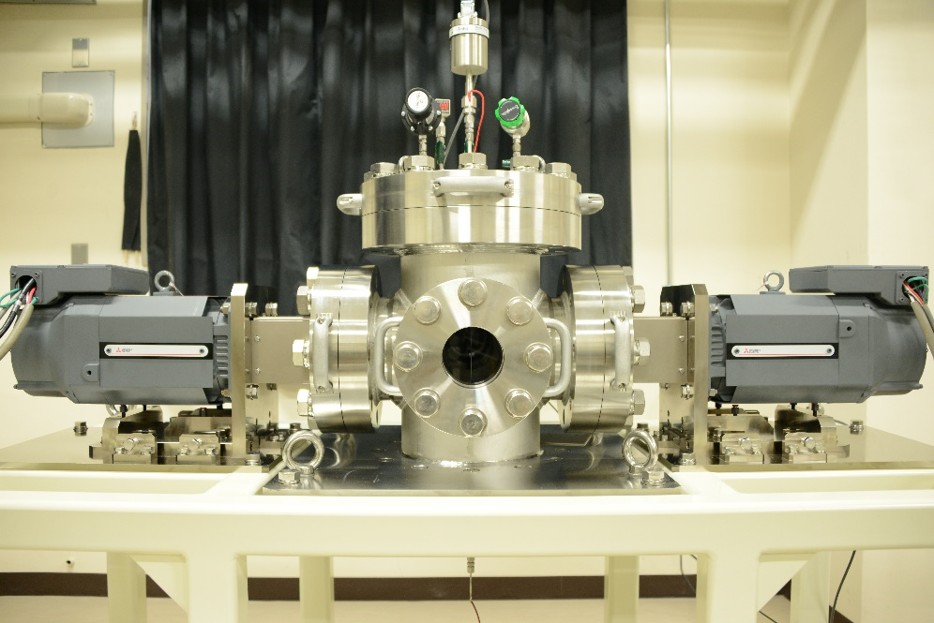 Experimental apparatus
Experimental apparatus
Related references
-
111.
Philipp Grajetzki, Takahiro Onda, Hisashi Nakamura, Takuya Tezuka, Kaoru Maruta, Investigation of the chemical and dilution effects of major EGR constituents on the reactivity of PRF by weak flames in a micro flow reactor with a controlled temperature profile, Combustion and Flame, Vol. 209, 13-26 (2019). doi:10.1016/j.combustflame.2019.06.021
-
108.
Philipp Grajetzki, Hisashi Nakamura, Takuya Tezuka, Susumu Hasegawa, Kaoru Maruta, A novel reactivity index for SI engine fuels by separated weak flames in a micro flow reactor with a controlled temperature profile, Fuel, Vol. 245, 429-437 (2019). doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2019.02.030
-
102.
Philipp Grajetzki, Hisashi Nakamura, Takuya Tezuka, Susumu Hasegawa and Kaoru Maruta, Evaluation of the reactivity of ultra-lean PRF/air mixtures by weak flames in a micro flow reactor with a controlled temperature profile, Combustion Science and Technology, Vol. 190, Issue 11:1950-1970 (2018). doi:10.1080/00102202.2018.1477772
